The Mediterranean diet, inspired by the traditional eating patterns of Mediterranean countries, has been extensively studied for its numerous health benefits. Among these, its positive effects on gut health stand out. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the intricacies of the Mediterranean diet and how it promotes a healthy gut microbiome.

Understanding the Mediterranean Diet
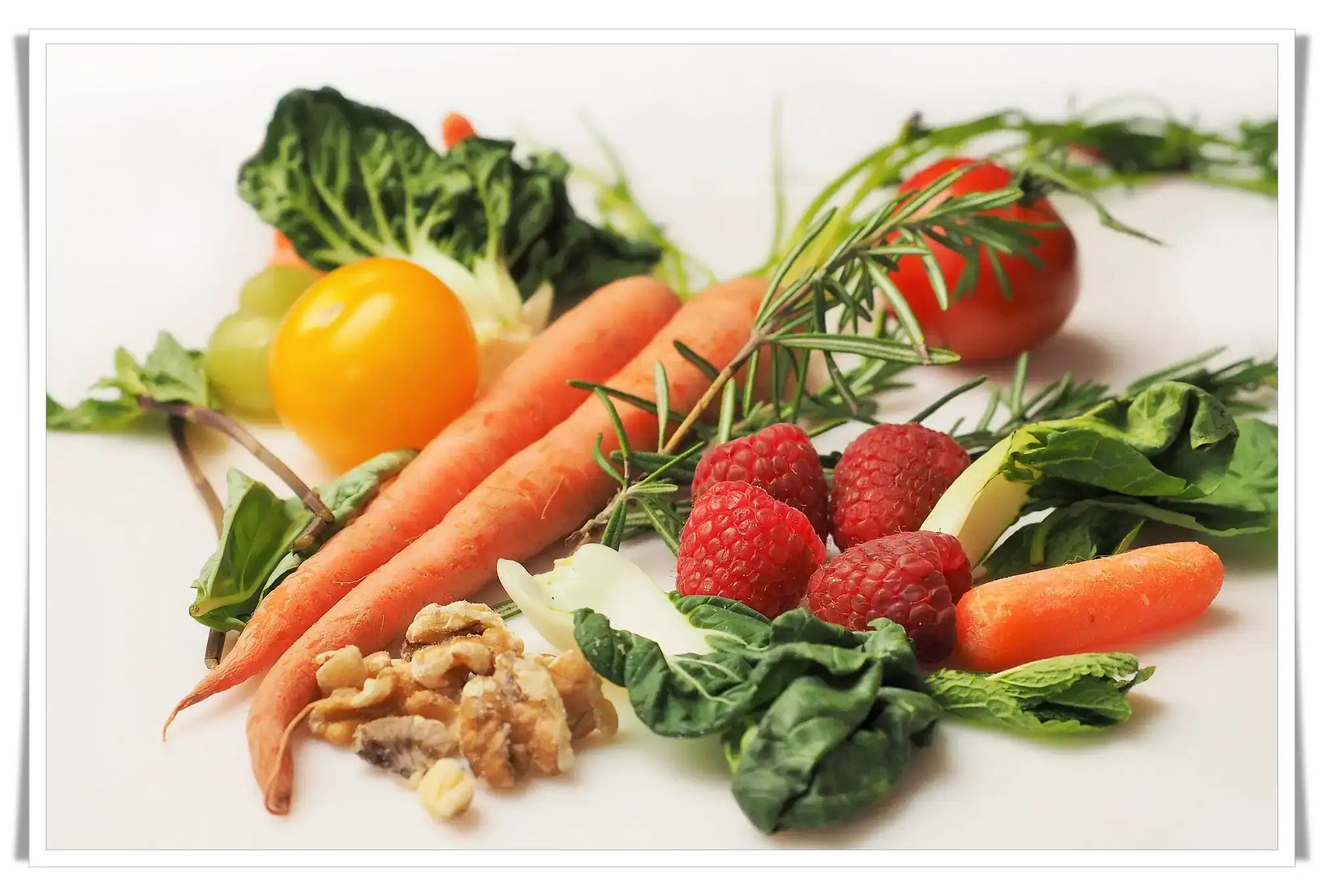
The Mediterranean diet is characterized by a high intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. It emphasizes healthy fats, particularly olive oil, and includes moderate consumption of fish and poultry, while limiting red meat and sweets. This dietary pattern is not only nutritionally rich but also diverse in flavors and textures.
Key Components of the Mediterranean Diet
- Fruits and Vegetables: Rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
- Whole Grains: Provide essential nutrients and promote satiety.
- Legumes: Excellent sources of protein and fiber.
- Nuts and Seeds: Packed with healthy fats, protein, and fiber.
- Olive Oil: A primary source of monounsaturated fats.
- Fish and Poultry: High-quality protein sources, rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
- Dairy: Usually consumed in moderation, often in the form of cheese and yogurt.
- Herbs and Spices: Enhance flavor without added sodium.
The Mediterranean Diet and Gut Health
Gut health is crucial for overall well-being, influencing digestion, immunity, and even mental health. The Mediterranean diet supports gut health through its high fiber content, diverse nutrients, and anti-inflammatory properties.
High Fiber Intake
The diet's emphasis on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes ensures a high intake of dietary fiber. Fiber acts as a prebiotic, feeding beneficial gut bacteria and promoting a healthy microbiome. This, in turn, aids in better digestion and prevents constipation.
Anti-inflammatory Properties
Olive oil, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish are rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants, which have anti-inflammatory effects. Chronic inflammation can disrupt the gut barrier and contribute to various gastrointestinal disorders. By reducing inflammation, the Mediterranean diet helps maintain gut integrity.
Polyphenols and Antioxidants
Fruits, vegetables, olive oil, and red wine (consumed in moderation) are rich in polyphenols and antioxidants. These compounds promote the growth of beneficial bacteria and inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria. Polyphenols also support the gut lining, enhancing its function and health.
Diverse Microbiome
A varied diet, as promoted by the Mediterranean dietary pattern, leads to a more diverse gut microbiome. A diverse microbiome is associated with better health outcomes, as it can perform a wide range of metabolic functions and adapt to changes in diet and environment.
Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet for Gut Health
Improved Digestion and Absorption
The high fiber content aids in regular bowel movements and prevents digestive issues such as constipation and bloating. A healthy gut microbiome, supported by the Mediterranean diet, improves the efficiency of nutrient absorption.
Enhanced Immune Function
A healthy gut microbiome is essential for a robust immune system. The anti-inflammatory and immune-modulating properties of the Mediterranean diet enhance the body's ability to fight infections and reduce the risk of autoimmune diseases.
Reduced Risk of Gastrointestinal Disorders
The Mediterranean diet has been linked to a lower risk of developing gastrointestinal disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and colorectal cancer. The diet's anti-inflammatory effects and support for a healthy microbiome play crucial roles in this protective effect.
Implementing the Mediterranean Diet
Practical Tips for Adopting the Mediterranean Diet
- Increase Fruit and Vegetable Intake: Aim for at least five servings of fruits and vegetables daily.
- Choose Whole Grains: Replace refined grains with whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole-wheat bread.
- Incorporate Legumes: Include beans, lentils, and chickpeas in your meals several times a week.
- Opt for Healthy Fats: Use olive oil as your primary cooking fat and snack on nuts and seeds.
- Moderate Protein Sources: Prefer fish and poultry over red meat and consume dairy in moderation.
- Flavor with Herbs and Spices: Use a variety of herbs and spices to add flavor without extra salt.
Sample Mediterranean Diet Meal Plan
Breakfast
- Greek yogurt with honey, walnuts, and fresh berries.
- Whole-grain toast with avocado and a drizzle of olive oil.
Lunch
- Quinoa salad with chickpeas, cucumber, tomatoes, olives, and feta cheese, dressed with olive oil and lemon juice.
- Whole-grain pita with hummus and a side of mixed greens.
Dinner
- Grilled salmon with a side of roasted vegetables and a mixed green salad.
- Whole-grain pasta with a tomato and basil sauce, topped with a sprinkle of Parmesan cheese.
Snacks
- Fresh fruit, such as an apple or orange.
- A handful of almonds or a small serving of olives.
The Mediterranean Diet and Mental Health
Emerging research suggests a strong link between gut health and mental health, often referred to as the gut-brain axis. The Mediterranean diet, by promoting a healthy gut, can also have positive effects on mental well-being.
Gut-Brain Axis
The gut-brain axis is a bidirectional communication system between the gut and the brain. This interaction involves the central nervous system, the autonomic nervous system, the enteric nervous system, and the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. A healthy gut microbiome plays a crucial role in this communication, influencing mood and cognitive functions.
For more detailed information on the components of the Mediterranean diet, you can visit the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
Impact of the Mediterranean Diet on Mental Health
Reduced Risk of Depression and Anxiety
Studies have shown that individuals following the Mediterranean diet have a lower risk of depression and anxiety. The diet's high content of omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and anti-inflammatory compounds supports brain health and reduces inflammation, which is linked to mood disorders.
Enhanced Cognitive Function
The Mediterranean diet is associated with better cognitive performance and a lower risk of cognitive decline and dementia. The diet's nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids, polyphenols, and vitamins, support brain function and protect against oxidative stress and inflammation.
Long-term Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet
Cardiovascular Health
The Mediterranean diet is well-known for its cardiovascular benefits. It reduces the risk of heart disease, lowers blood pressure, and improves cholesterol levels. These benefits are largely due to the diet's emphasis on healthy fats, fiber, and antioxidants.
Weight Management
Adopting the Mediterranean diet can aid in weight management. The diet promotes satiety through high fiber and healthy fat intake, which helps control appetite and reduce overeating. Additionally, the diet encourages physical activity and mindful eating, further supporting weight management goals.
Diabetes Prevention and Management
The Mediterranean diet helps prevent and manage type 2 diabetes. Its high fiber content stabilizes blood sugar levels, while healthy fats and protein sources improve insulin sensitivity. The diet's emphasis on whole, unprocessed foods also reduces the risk of developing metabolic syndrome.
Longevity
Numerous studies have linked the Mediterranean diet to increased longevity. The diet's comprehensive approach to nutrition, combined with an active lifestyle and strong social connections, contributes to a longer, healthier life.

Challenges and Considerations
Accessibility and Cost
While the Mediterranean diet is rich in fresh fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats, these items can be expensive or hard to find in some areas. It's important to find affordable and accessible alternatives that fit within the Mediterranean dietary pattern.
Adaptation and Sustainability
Transitioning to a Mediterranean diet requires significant changes in eating habits. It’s essential to make gradual adjustments and find ways to incorporate Mediterranean principles into daily meals to ensure long-term adherence.
Cultural and Personal Preferences
The Mediterranean diet may need to be adapted to fit different cultural and personal preferences. The key is to maintain the core principles of the diet while incorporating a variety of foods that are culturally appropriate and personally enjoyable.
For more detailed information on the components of the Mediterranean diet, you can visit the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
Practical Steps to Embrace the Mediterranean Diet
Start Small
Begin by making small changes, such as incorporating more fruits and vegetables into meals, using olive oil for cooking, and choosing whole grains. Gradually increase these changes until they become a regular part of your diet.
Experiment with Recipes
Explore Mediterranean recipes and experiment with new ingredients and cooking methods. This can make the transition enjoyable and help you discover new favorite dishes.
Involve the Family
Encourage family members to join you in adopting the Mediterranean diet. Cooking and eating together can make the process more fun and sustainable.

Plan and Prepare
Plan your meals and snacks ahead of time to ensure you have healthy options available. Preparing meals in advance can help you stay on track, especially during busy days.
Conclusion
The Mediterranean diet offers a holistic approach to health, benefiting not only the gut but also mental health, cardiovascular health, weight management, and overall longevity. By embracing this dietary pattern, individuals can achieve a healthier, more balanced lifestyle. Start small, stay consistent, and enjoy the rich, diverse flavors of the Mediterranean diet for optimal health and well-being.
The Mediterranean diet is a powerful tool for promoting gut health. Its rich diversity of nutrients, high fiber content, and anti-inflammatory properties support a healthy and diverse gut microbiome. By adopting this dietary pattern, individuals can improve their digestion, enhance their immune function, and reduce the risk of gastrointestinal disorders. Embrace the Mediterranean way of eating for a healthier gut and overall well-being.